Table of contents
User Experience (UX) is the cornerstone of successful design, and understanding the fundamental principles that drive user satisfaction is crucial. UX heuristics provide designers with a set of guidelines to create intuitive and engaging experiences. 10 UX heuristics can elevate our design process and help us craft exceptional user experiences.
Visibility of System Status
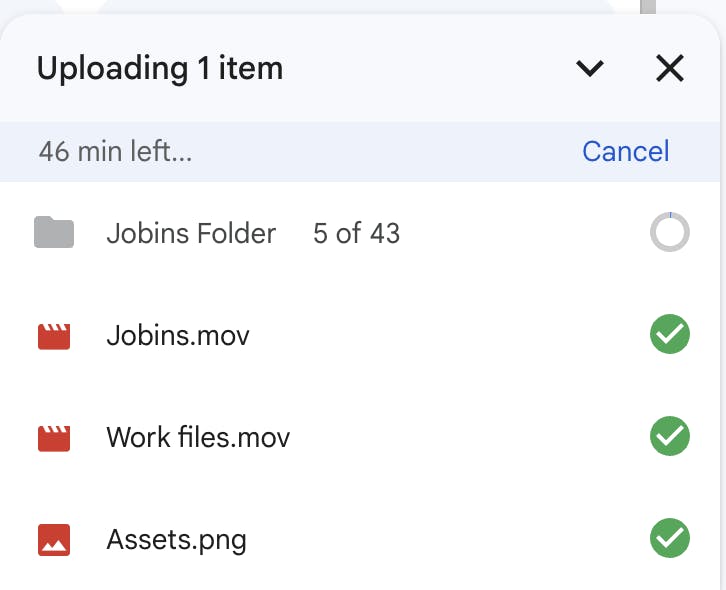
Users should always be aware of what's happening within the system. Utilize visual cues, progress indicators, and loading animations to provide real-time feedback on actions and processes. By keeping users informed, a seamless and transparent interaction is ensured.
Example: When uploading a file to a cloud storage service like Google Drive, a progress bar provides users with real-time feedback on the upload process. This visibility reassures users that their action is being processed, enhancing their confidence and reducing uncertainty.
Match Between System and the Real World
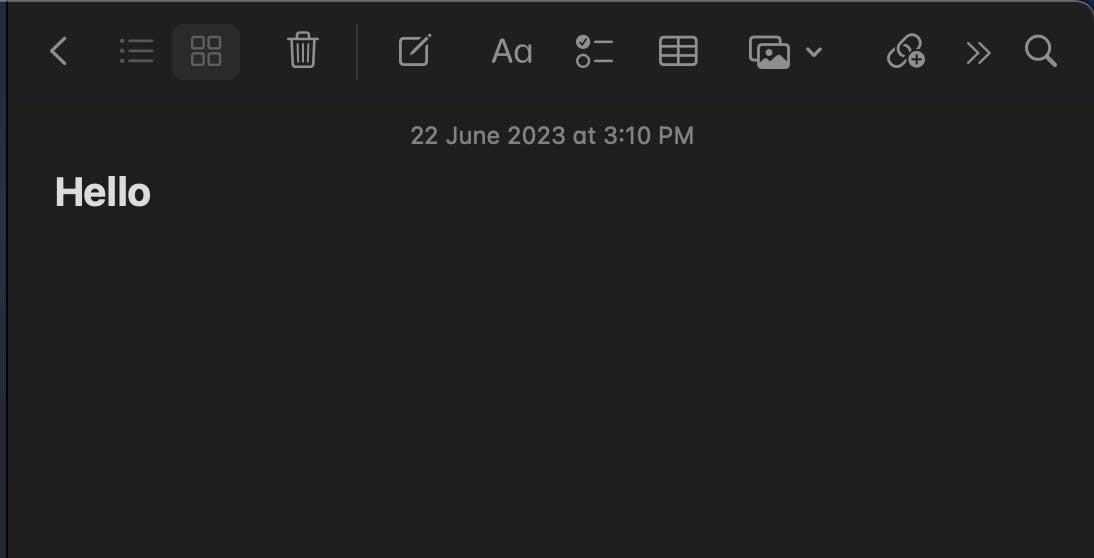
Design systems that align with users' mental models and their understanding of the real world. Use familiar language, icons, and interactions that resemble real-world objects and actions. By bridging the gap between the digital and physical realms, you enhance usability and reduce cognitive load.
Example: In digital note-taking apps such as Apple Notes, using a "Trash" icon to represent deleting a note aligns with users' mental models of discarding physical items in a trash bin. This familiar metaphor makes the action of deleting notes intuitive and recognizable.
User Control and Freedom
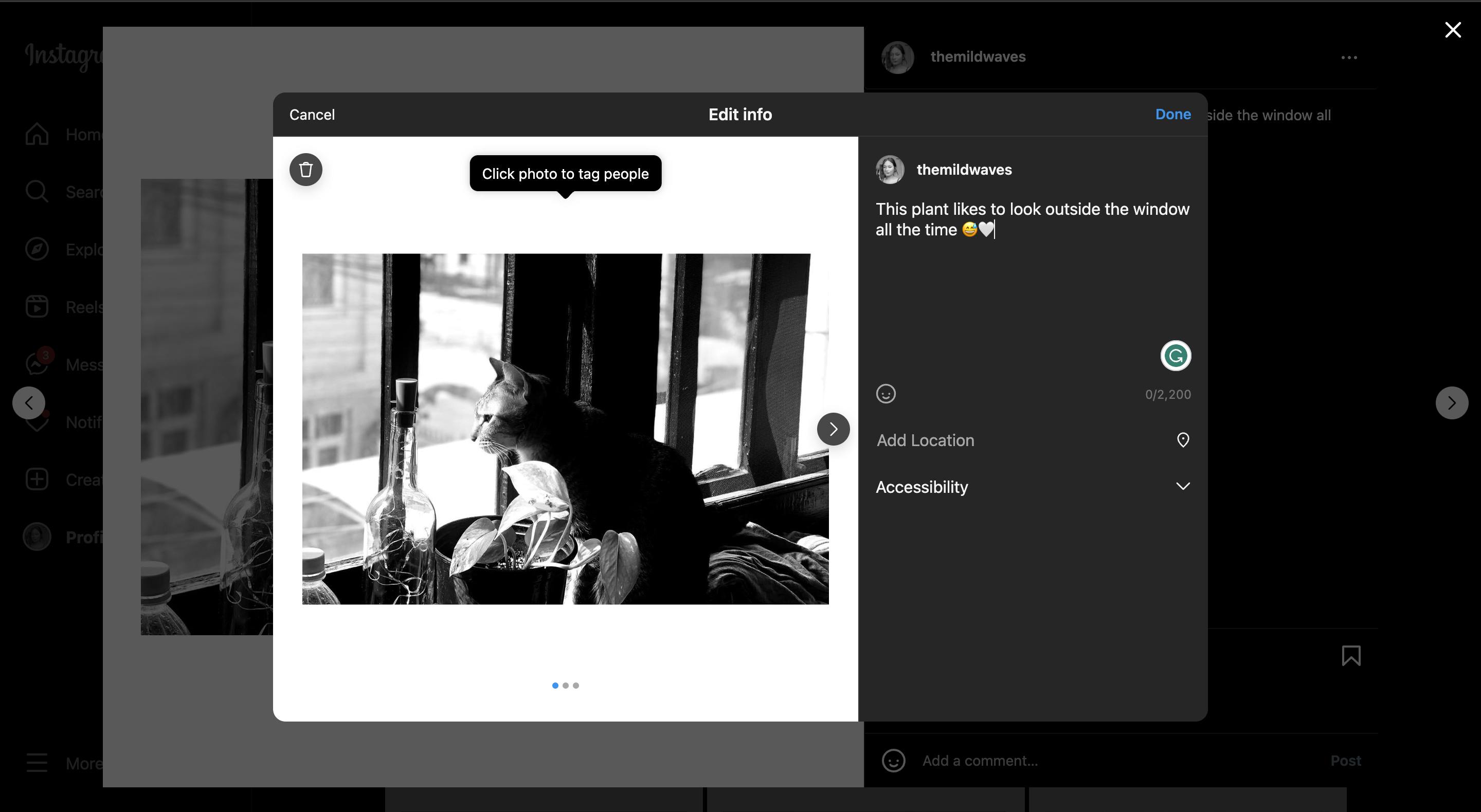
Empower users with control over their actions and enable easy navigation. Offer clear and accessible options to undo, redo, or cancel actions, allowing users to explore and experiment without fear of irreversible consequences. By providing freedom, you enhance user confidence and overall satisfaction.
Example: Instagram provides users with control and freedom over their posts by allowing them to edit and modify their content even after it has been shared. With the presence of an "Edit" or "Back" button, users can easily make changes, correct mistakes, or update their selections without the need for restarting the entire process. This feature ensures a seamless and hassle-free experience, giving users a sense of reassurance and control over their shared content.
Consistency and Standards
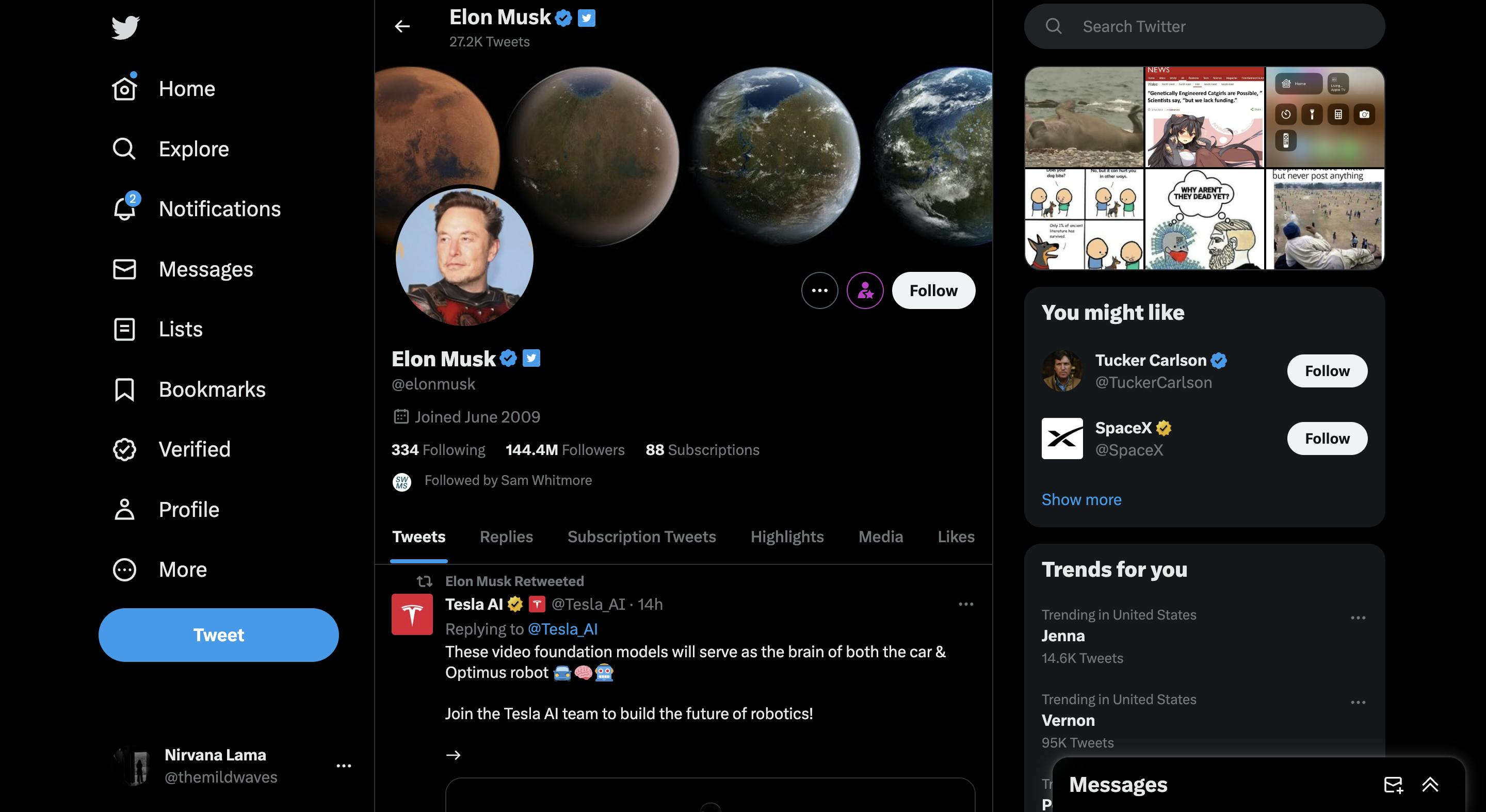
Maintain consistency in design elements, interactions, and terminology throughout your product. Users rely on consistent patterns and conventions to navigate interfaces. By adhering to industry standards and leveraging established design patterns, you create a familiar and intuitive user experience, reducing friction.
Example: Social media platforms like Twitter and Facebook use a consistent layout for user profiles, with profile pictures on the left, a brief bio, and tabs for different types of content. This adherence to a standard profile design pattern ensures users can quickly navigate and find the information they need.
Error Prevention and Handling
Design with error prevention and recovery in mind. Implement validation mechanisms, provide real-time feedback, and offer clear error messages. Guide users towards error-free interactions and help them correct mistakes effectively without losing their progress. A seamless error-handling process enhances user trust and satisfaction.
Example: When filling out a web form, if a user forgets to fill in a required field and tries to submit it, a form validation message appears near the empty field, notifying the user of the error. This proactive error prevention technique helps users identify and rectify mistakes before submitting the form.
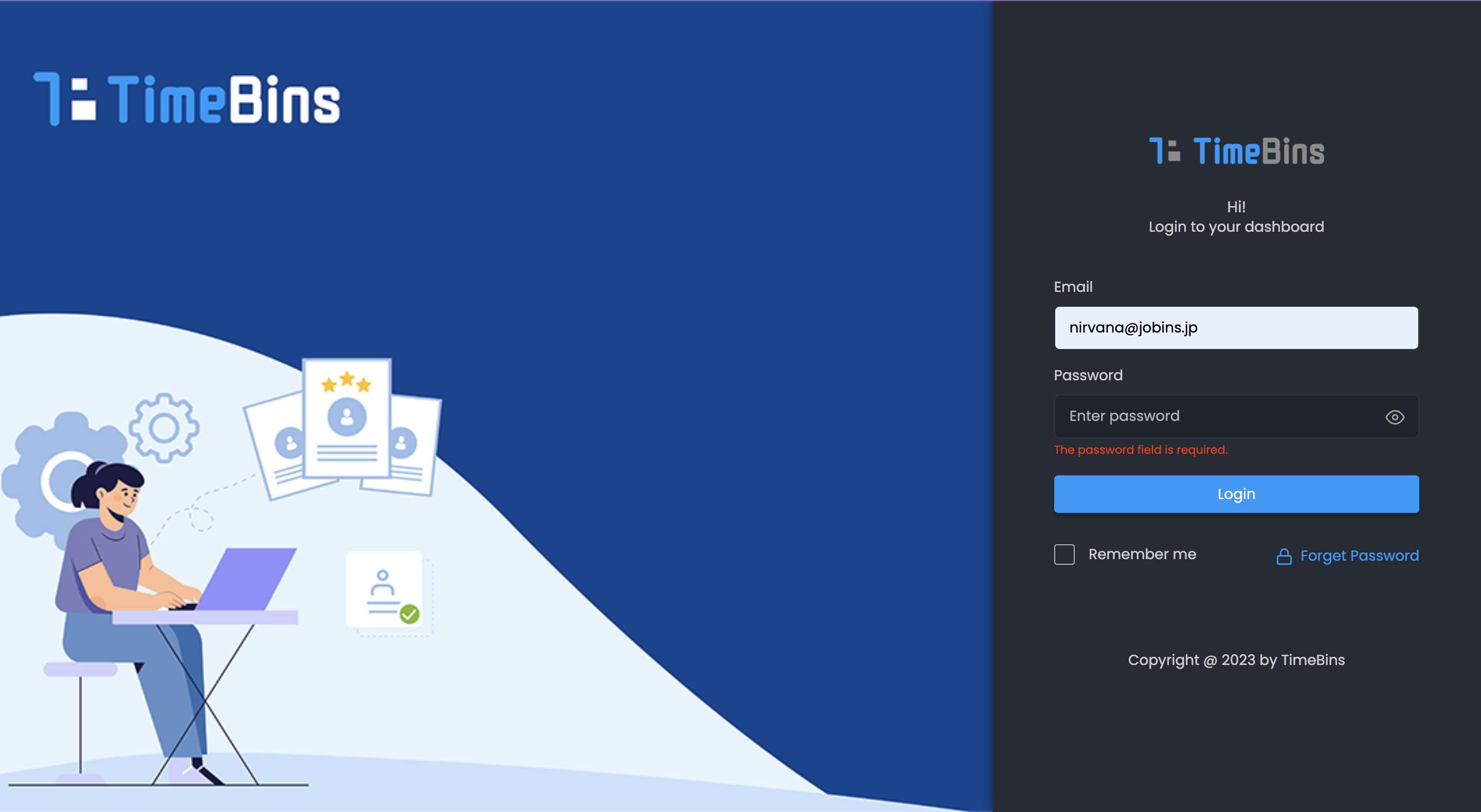
Recognition Rather than Recall
Minimize the cognitive load on users by presenting information and options in context. Avoid relying on users' memory and instead provide visual cues, labels, and relevant information that eliminate the need for users to remember or recall previous actions. By reducing the effort required, you create a smoother and more intuitive user experience.
Example: Navigation menus with visible labels and icons, such as the "Hamburger" menu, provide users with visual cues for recognizing different sections or features within an application. By minimizing the need for users to recall specific options, the navigation becomes more intuitive and efficient.
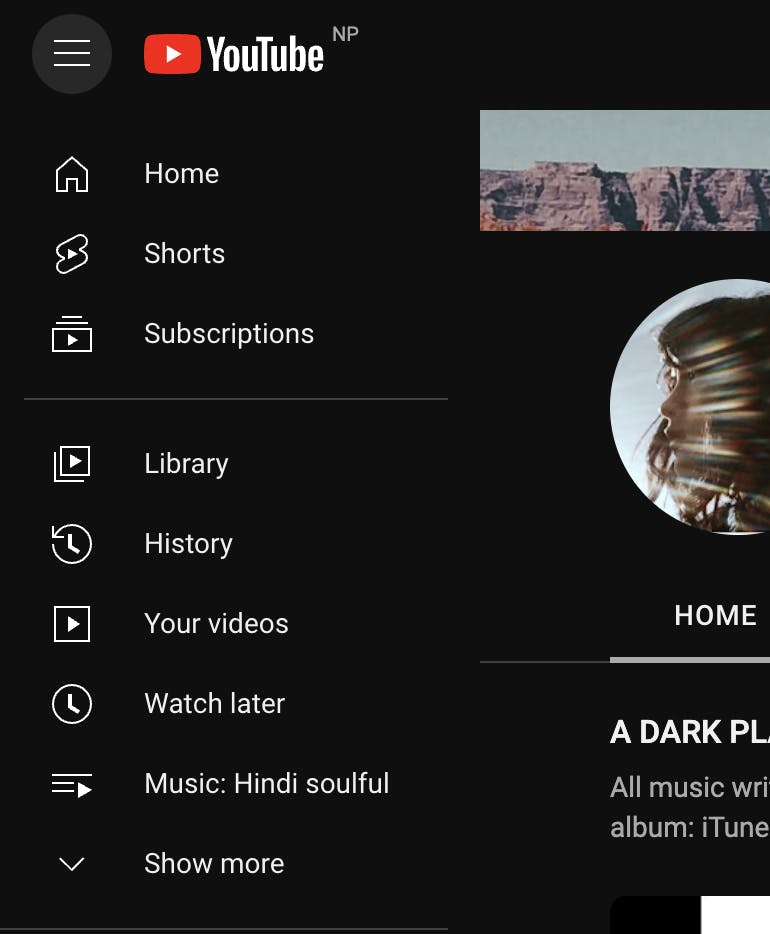
Flexibility and Efficiency of Use
Consider the needs of both novice and experienced users by providing flexible and efficient interaction options. Incorporate shortcuts, customizable features, and advanced functionalities that allow power users to accomplish tasks quickly. At the same time, ensure the system remains accessible and usable for all users, regardless of their expertise.
Example: In a music streaming app like Spotify, personalized playlists and recommendations based on the user's listening history and preferences are added. This customization feature allows users to discover new music tailored to their tastes, enhancing their enjoyment of the app.
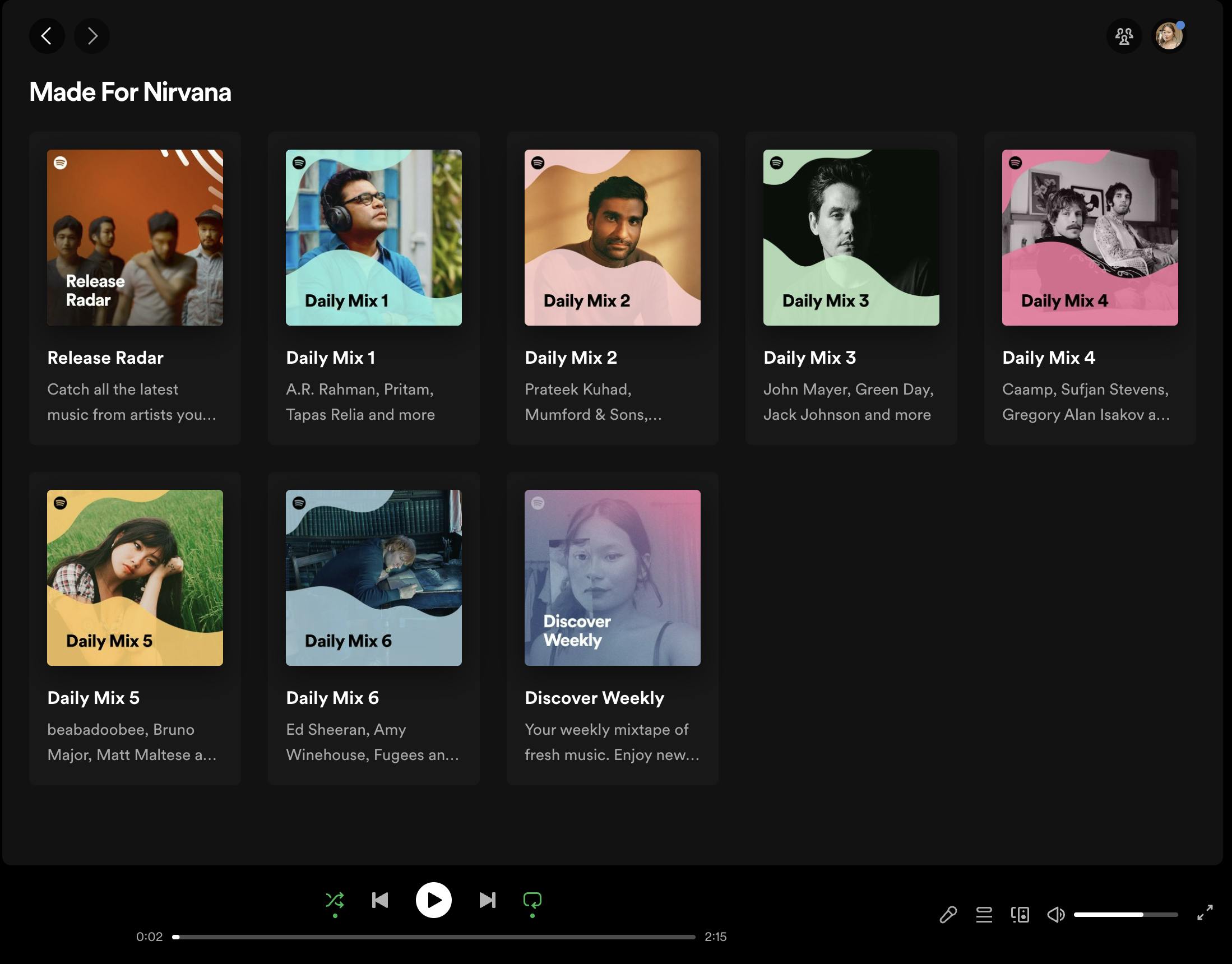
Aesthetic and Minimalist Design
Create visually appealing interfaces with a minimalist design approach. Reduce clutter and unnecessary elements to maintain a clean and focused user interface. Use appropriate typography, balanced color schemes, and well-structured layouts to enhance usability and create a delightful user experience.
Example: The Apple website embraces a minimalist design approach with clean lines, ample white space, and a focus on product imagery. This aesthetic choice creates a visually pleasing and uncluttered experience, allowing users to concentrate on the products and their features.
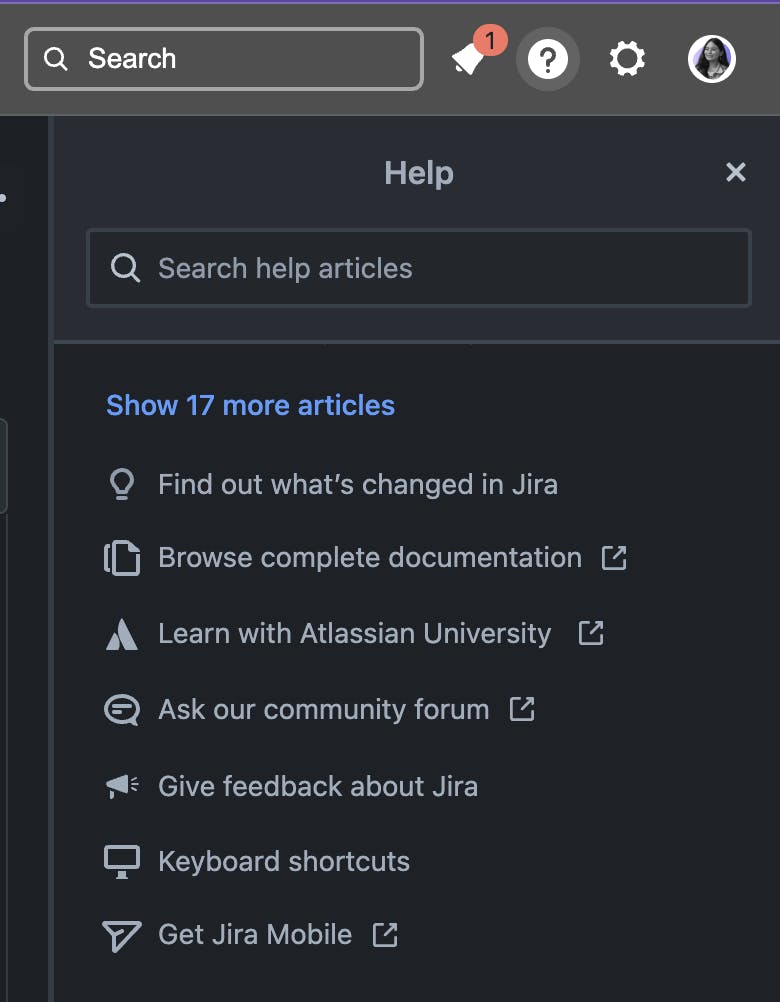
Help and Documentation
Offer contextual help and documentation to assist users throughout their journey. Provide clear instructions, tooltips, and onboarding experiences to guide users through complex tasks or unfamiliar features. Well-designed help resources empower users to explore the product's full potential and overcome obstacles.
Example: Project management tools like Jira offer contextual help through interactive tooltips or guided tours that introduce users to key features and functionalities. By providing on-the-spot guidance and explanations, users can quickly understand how to use the app effectively without the need for extensive external documentation.
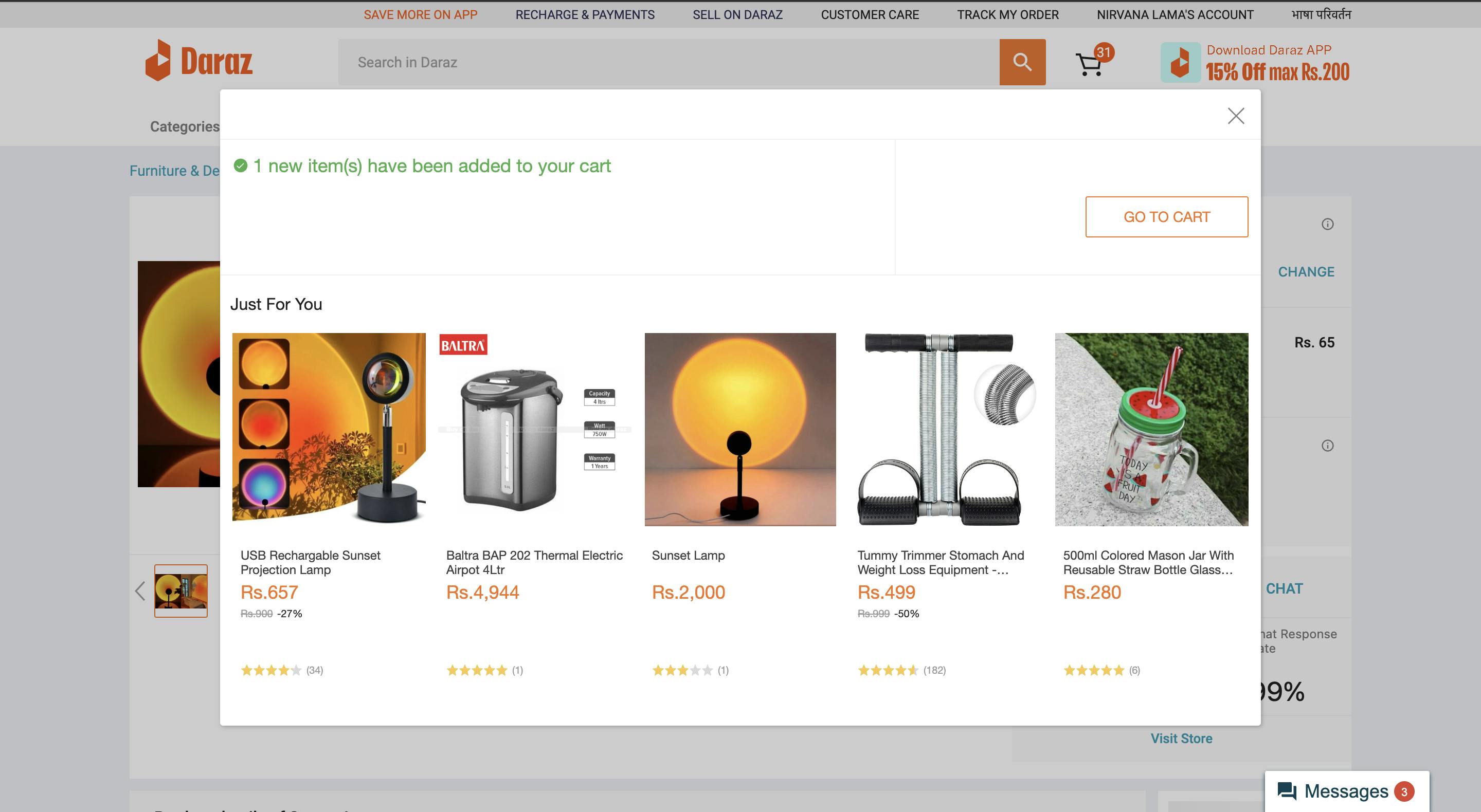
Feedback and Response Time
Ensure timely responses to user actions. Minimize latency and optimize system performance to provide instantaneous feedback. Users appreciate interfaces that respond promptly and predictably, as it enhances their perception of the product's reliability and usability.
Example: In an e-commerce platform like Daraz, when users click the "Add to Cart" button, it is crucial to provide them with prompt and responsive feedback. This immediate confirmation assures users that their selected item has been successfully added to the cart, enhancing their overall satisfaction and confidence in the platform's reliability.
Conclusion
UX heuristics serve as valuable guidelines for designers to create user-centric interfaces that are intuitive, efficient, and enjoyable. By embracing these ten heuristics, we can elevate our design process and build exceptional user experiences.
The key to successful UX design lies in understanding and empathizing with the users, prioritizing their needs, and refining designs to deliver delightful interactions.
