In order to pursue a career as a User Experience (UX) designer, it's essential to grasp the significance of UX, comprehend its purpose, and have a clear understanding of the responsibilities associated with being a UX designer.
History of UX Design

Around 500 BC, Ancient Greeks pioneered the Ergonomic principles for designing tools and constructing theaters. Ergonomics, in this context, involves comprehending the interactions among humans and various elements within a system. In the 1940s, Taylorism management advocated task division for efficient completion, but Toyota's Taichi Ohno, a Japanese industrial engineer, shifted towards a human-centered design approach. As time progresses, there's a growing recognition of the significance of user-centric design.
In the early 90s, cognitive scientist Donald Norman became Apple's first User Experience Architect, coining the term "user experience design" to encompass the entirety of user interactions. His 1988 book, The Psychology of Everyday Things (later updated to The Design of Everyday Things), remains a UX design cornerstone, delving into practical design elements like affordances, signifiers, and feedback.
What is User Experience (UX) ?
In a simple word, Everything that touches upon your experience either it may be goods, services OR products is User Experience. The essence of UX is to guarantee that users discover meaningful value what you are offering to them.
Lets understand why UX is important:
UX endeavors to meet user needs, fostering a journey of enhanced customer satisfaction, conversion, and retention.
UX helps to create positive user experiences that encourage loyalty to the product or brand.
UX describe customer journeys within your product, establishing a mutual relationship between the creator and the user.
UX contributes to cost reduction in development, bug fixing, marketing, and other aspects.
UX focus HCD (Human Centric Design).
Innovation isn't always necessary; user-focused design can make a product stand out by presenting familiar ideas uniquely.
UX facilitates an intuitive experience, coherence, continuity, and platform-specific designs.
The 5 Elements of UX Design
The UX design process involves a structured framework known as the five elements, guiding UX designers from concept to a functional product. These elements, arranged from bottom to top, include strategy, scope, structure, skeleton, and surface.
Strategy: What issue does this product aim to address? This layer, the most abstract within the model, considers the alignment of user needs and business objectives.
Scope: What product will be developed to address the problem? In this layer, the team outlines functional requirements (features to build) and content requirements (written and visual information to include).
Structure: How is the design structured, and what is the interaction flow like? This layer encompasses information architecture (content structure and organization) and interaction design (the interactive experience of the product).
Skeleton: How is information displayed and organized? This layer starts to address UI design (interface element design), navigation design (user system movement), and information design (presenting information for clarity). A typical outcome at this stage is a collection of wireframes.
Surface: What is the visual and experiential impact on users? This phase focuses on visual design, including color choices and typefaces, and prominently features UI design, though it extends beyond the surface aspect.
User Experience Vs User Interface Design (UX vs UI)
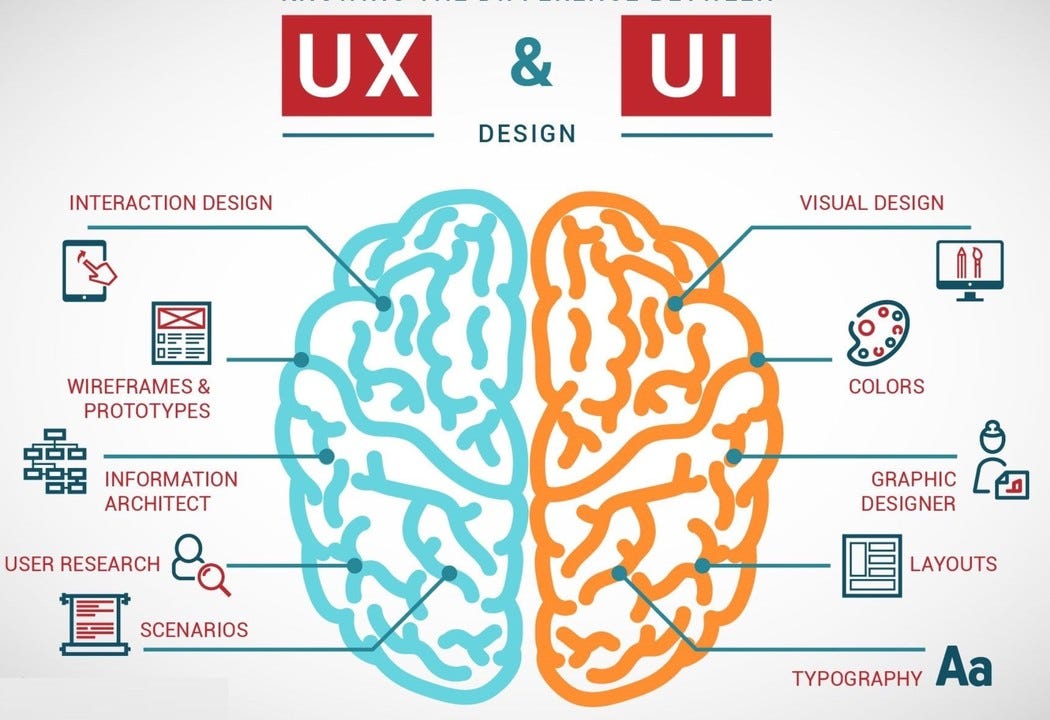
In the field of digital design, UX and UI play separate yet complementary roles. UX is focused on understanding user psychology, cognitive flow, and ensuring task completion with an emphasis on creating an intuitively interactive experience. On the other hand, UI concerns to the components that constitute the interface, including colors, typography, buttons, lists, and text fields. Its primary goal is to highlight the simplicity of interaction, thereby enriching the user's journey guided by the principles of UX.
Below is a table outlining the key distinctions between UX and UI design.
| Aspect | UX Design | UI Design |
| Focus | Overall user experience, satisfaction, and journey. | Visual elements, aesthetics, and interactivity. |
| Concerns | User psychology, task completion, and cognitive flow. | Buttons, icons, colors, typography, and layout. |
| Goal | Intuitive and enjoyable interaction for users. | Visually appealing and user-friendly interface. |
| Testing | Usability testing, user feedback, and iterative design. | Prototyping and testing visual design elements. |
This table provides a concise overview of the main differences between UX and UI design, helping to clarify their distinct roles and focuses.
Conclusion
Congratulations! 🎉 You have now gained a comprehensive overview of basics of UX design. Understanding the distinct yet interconnected roles of User Experience (UX) and User Interface (UI) design is essential for creating digital products that not only look visually appealing but also provide a seamless and enjoyable user experience.
With this knowledge, you are better equipped to appreciate the intricate balance between the psychological aspects of user interaction (UX) and the visual elements that constitute the interface (UI).
As you dive further into the world of digital design, keep in mind the collaborative nature of UX and UI, working hand in hand to craft engaging and user-centric solutions.
Happy designing 👨💻

